Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
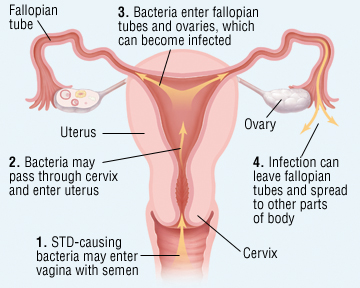
Definition: It is the polymicrobial infection and inflammation of the upper genital tract typically involving the fallopian tubes, ovaries and surrounding structures (endometritis, salpingitis, pelvic peritonitis, tubo-ovarian abscess).
Causative organisms:
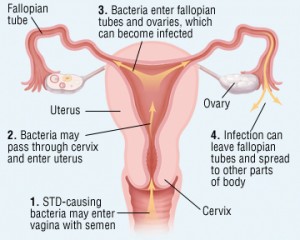 Primary organisms: Ascending spread of micro-organisms from cervico-vaginal canal
Primary organisms: Ascending spread of micro-organisms from cervico-vaginal canal
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (1/3rd cases)
- Chlamydia trachomats (1/3rd cases)
- Mycoplasma hominis (1/10th cases)
Secondary organisms:
- Endogenous aerobes: Non-hemolytic streptococcus, E.coli, Group B streptococcus, Staphylococcus
- Endogenous anaerobes: Bacteroides, Peptostreptococcus, Peptococcus
Risk Factors:
- Young, nulliparous, sexually active women with multiple sex partners for whom we also recommend this hiv test kit
- Douching
- Prior PID
- IUD use
- Iatrogenic procedures: Endometrial biopsy, Uterine curettage, Hysterosalpingography
Protective Factors:
- Contraceptive: OCPs and Barrier methods
- Menopausal, pregnant with monogamous partner
Symptoms:
- Lower abdominal and pelvic pain (dull)
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting (indicates peritonitis)
- Menstrual disturbances
- Purulent cervical discharge
- Dyspareunia
- RUQ pain indicates perihepatitis (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome)
Signs:
- Vitals: Elevated temperature > 38c
- Abdominal palpation: Bilateral lower abdominal tenderness
- Vaginal examination:
- Purulent vaginal discharge
- Congested external urethral meatus or openings of Bartholin’s ducts
- Speculum examination: Congested cervix with purulent discharge
- Bimanual examination:
-
- Chandelier sign: Cervical motion tenderness
- Adnexal tenderness
- Thickening or definite mass
Minimum clinical criteria for diagnosis
- Cervical motion tenderness
- Uterine tenderness
- Adnexal tenderness
The presence of temperature higher than 38.3° C (101° F) and abnormal cervical or vaginal mucopurulent discharge enhance the specificity of the minimum criteria, as do selected laboratory tests.
Investigations and Diagnosis:
- Identification of organisms:
- Endocervical swabs (Gram stain and culture)
- Urine microscopy and culture
- Lab:
- WBC > 10,000/cu.mm
- ESR > 15mm/hr
- Raised CRP
- Serological test for syphilis: on both partners
- Ultrasonography: To rule out tubo-ovarian abscess
- Laparoscopy: To rule out appendicitis or ectopic pregnancy and to aspirate fluid for analysis
- Indicated if diagnosis is uncertain or failure to respond to antibiotic therapy within 48-72 hours
- Laparotomy: It is strongly recommended if
- Patient > 40 years
- Recurrent PID attacks
- History of tubal ligation
- Other:
- Saline microscopy of cervical or vaginal discharge
- B-hCG: To rule out pregnancy (ectopic pregnancy)
- Pelvic CT and MRI (not routinely recommended)
Differential diagnosis:
- Acute appendicitis
- Adnexal torsion (Ovarian torsion)
- Diverticulitis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Endometritis
- UTI
Adler sign: For distinguishing appendicitis from adnexal or uterine pain, if the point of maximal tenderness shifts medially with repositioning on the left lateral side, etiology is generally gynecologic
Complications:
- Immediate: Pelvic/Generalized peritonitis, Septicemia
- Late: CDEF
- Chronic PID
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Dyspareunia
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Fertility impaired (Infertility)
Treatment:
All sex partners examined and treated appropriately
Outpatient antibiotic therapy: Oral therapy
- Regimen A: Cefoxitin 2gm im + Probenecid 1gm oral X 1 dose
- Regimen B: Ceftriaxone 250 mg im X 1dose + Doxycycline 100mg BD X 14 days
- Regimen C: Ofloxacin 400 mg bd + Metronidazole 500 mg X 14 days
Inpatient antibiotic therapy: IV therapy
- Indications: PID
- Pelvic abscess
- Pregnancy
- Immunodeficient: HIV or Immunosuppresive
- Intolerance or Unresponsive to Outpatient antibiotic therapy
- Illness: Severe illness, high fever
- Diagnosis uncertain: Surgical emergencies (ectopic pregnancy and acute appendicitis) cannot be ruled out
- Regimen A: Cefoxitin 2gm iv 6 hrly OR Cefotetan 2gm iv 12 hrly + Doxycycline 100 mg iv or orally 12 hrly X 14 days
- Regimen B: Clindamycin + Gentamycin X 14 days
Surgery:
- Tubo-ovarian abscess:
- NG tube, IV fluids, Investigations
- Antibiotics: Ofloxacin 400 mg iv 12 hrly + Metronidazole 500 mg orally or iv 8 hrly OR Imipenem 500 mg iv 6 hrly
- Surgical excision
- Transcutaneous/Transvaginal aspiration
- Overwhelming infection or Chronic intractable pelvic pain:
- Hysterectomy and BSO
Follow up:
- Repeat smears and cultures after 7 days of discharge
- Repeat following each menstrual period until it becomes negative for 3 consecutive reports
Gainesville staging of Acute PID:
- Stage I: Acute endometritis-salpingitis without peritonitis
- Stage II: Acute salpingitis with peritonitis
- Stage III: Acute salpingitis with superimposed tubal occlusion
- Stage IV: Ruptured tubo-ovarian abscess or tubo-ovarian complex
- Stage V: Respiratory complications
Therapeutic goals:
- Stage I: Eliminate symptoms and infectivity
- Stage II: Preservation of fallopian tube function
- Stage III: Preservation of ovarian function
- Stage IV: Preservation of patient’s life
For Stage III and IV: An antimicrobial cover with at least 3 drugs i.e., beta –lactam, clindamycin and tobramycin, should be provided. If there is a deterioration in the patient’s condition, rupture of an abscess should be considered and surgical exploration is recommended.


4 Comments
Simple and straight to the point, thank you
Great stuff…used it for osce
excellent summary. much appreciated
simplified and adequate.
Comments are closed.