Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)

Premenstrual Syndrome ( PMS):- Cause, Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment.
Know it : also called PMT or premenstrual tension
They are spectrum of symptoms that occur just prior to menstruation. The causes of these symptoms have not been well defined. The Symptoms occur cyclically in last 7-10 days of the menstrual cycle. PMS can cause significant distress and alter daily activities.

To Define PMS, following criteria must be fulfilled:-
1. There is no related Organic Lesion
2. Cyclically occurs during the luteal phase of each menstrual cycle ( 2nd half of cycle)
3. Symptoms are severe enough to affect lifestyle and requires medical help
4. During rest of the Cycle, she is Symptom free.
Epidemiology:
While 80% of menstruating women have experienced at least one symptom that could be attributed to PMS, estimates of prevalence range from as low as 3% to as high as 30%. Exact data on Nepal is not known, but it is comparable to worldwide statistics.
Cause:
Not exactly known, but following pathogenesis have be postulated:-
1. Alteration in levels of Estrogen and Progesterone which starts in mid cycle. ? Diminished Progesterone level is also suspected.
2. Neuroendocrine Factors: Role of Serotonin, Endorphins and GABA
3.Psychological and Psychosocial factors may have role as well.
Clinical Features Of PMS:
Usually women in age groups 30-45 years are affected. It often may be related to Childbearing or disturbing life event.
Symptoms:
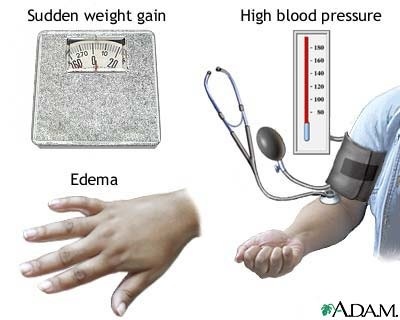
- Abdominal Bloating, Swelling of Extremities, Weight gain, and Breast tenderness are common complains.
- Features of Emotional Instability like Irritability, Depression, Insomnia, Dyspareunia and Anxiety.
- Tension headache and loss of Concentration have been seen
On Examination:- There is no abnormal pelvic pathology, but pelvic congestion may occur.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis is Confirmed if GnRH analogue, Goserelin 3.6 mg in form of Depot at monthly intervals for 3 cycles, given relieves symptoms.
TREATMENT OF PMS:
Advice:
- Assurance
- Avoid salt, caffeine, and alcohol specially in second half of cycle
- Tranquillizers and Anti-depressant s may help. Alprazolam and Fluoxetine are used.
- Pyridoxine 100mg BD is helpful
- Diuretics- Frusemide 20 mg OD for 5 days in second half of Cycle for water retention symptoms.
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers may help ease physical symptoms, such as cramps, headaches, backaches, and breast tenderness. These include:
- Ibuprofen
- Ketoprofen
- Naproxen
- Aspirin
Certain vitamins and minerals have been found to help relieve some PMS symptoms. These include:
- Folic acid
- Calcium with vitamin D
- Magnesium
- Vitamin B-6
- Vitamin E
Hormonal Management of Premenstrual Syndrome:
- Oral Contraceptive Pills- 3-6 cycles. Suppress ovulations and maintains uniform hormonal ratio.
- Progestogen: Dydrogesterone 10 mg daily or BD from 5 – 20 days of cycle . Lng-IUS ( Levonorgesterol Intrauterine Device) are used as Progesterone deficiency is a posthulated cause.
- Bromocriptine: 2.5 mg daily or BD may be helpful,specially for breast complains.
SUPPRESSION of Ovarian Cycle:
Danazol
GnHR Analogues- Goserelin, Buserili, Leuprorelin acetate, Triptorelin.
SURGICAL Management :
– Oophorectomy (Removal of Ovaries)
– Hysterectomy with Bilateral Oophorectomy is the last Resort.
Prognosis:
- PMS is generally a stable diagnosis, with susceptible women experiencing the same symptoms at the same intensity near the end of each cycle for years.
- Treatment for specific symptoms is usually effective at controlling the symptoms. Even without treatment, symptoms tend to decrease in perimenopausal women, and disappear at menopause.
- Women who have PMS have an increased risk for Depression
Source: DC Dutta Gynaecology, Wikipedia, womenshealth.gov