What Is A Contract Research Organization And What Does It Do?
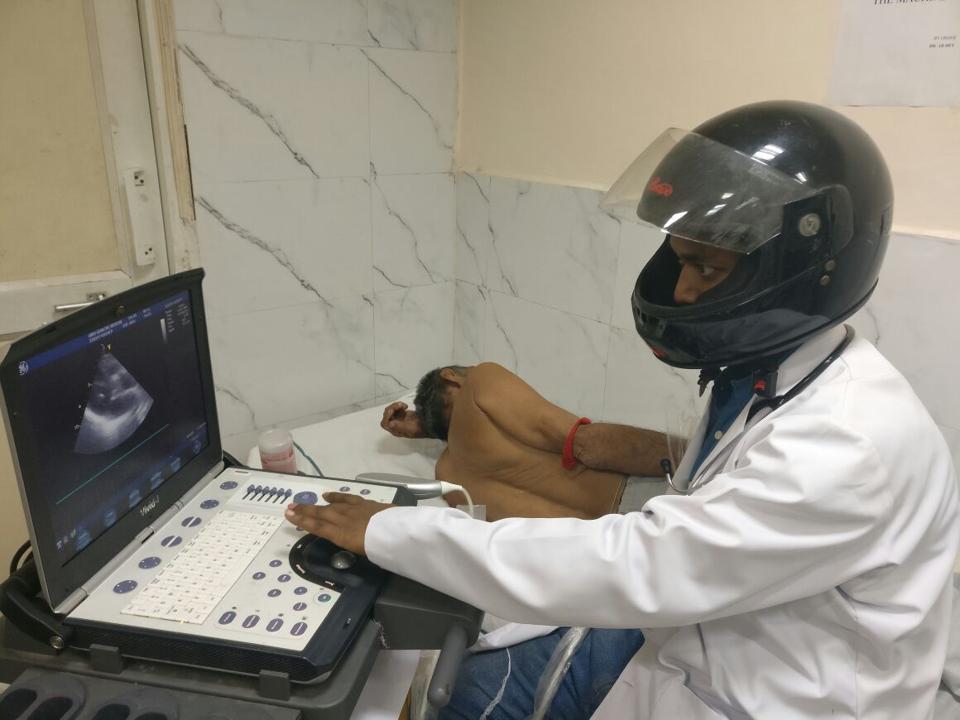
Contract research organizations (CROs) work to provide research support for a variety of health care through clinical trials. They assist medical devices, biotechnology, and pharmaceutical industries, as well as universities, private foundations and government agencies.
Essentially, a contract research organization is a third-party outsource company rather than an in-house extension of an organization’s research division. It is a cost-effective way for organizations to outsource highly specialized functions related to health-care research or medical manufacturing.
2 Examples of Clinical Trial Support
Here are two examples to illustrate how a CRO can help its clients:
- A CRO might provide clinical trials to support a pharmaceutical company that has just developed a new medication. The pharmaceutical company may not have enough staff, facility space, or other essential resources to do the clinical study themselves, but it’s necessary for them to verify the efficacy of their new formula to get FDA approval.
- A CRO might provide clinical trials to support a team of medical researchers interested in developing treatments for cancerous tumors. The researchers need clinical trials to prove or disprove their hypothesis.
Benefits of Hiring A CRO
Organizations contract with a CRO for a wide number of reasons, ranging from expediency to economics:
A company might outsource the support they need to a CRO for the following reasons:
- · The organization needs clinical trials and specialized functions outside of the business’ own scope.
- · The organization does not have to hire permanent staff when they need people with specific knowledge and skills for a new project.
- · The organization may outsource the services they need even when they have the resources in-house because a CRO can do it faster, more efficiently, and at a lower price.
- · The organization may not have the office or laboratory space to run a trial themselves.
- · The organization may have staff that is preoccupied with other projects and therefore does not have enough available people to run their own clinical trials on a new research project.
A Brief Overview of CROs
- Scope of work:
Not all CROs are the same. Some are highly specialized, focusing on only a few key aspects of clinical trials. Others manage every aspect of a clinical trial from the ground up. In other words, some may be small and niche focused while others are large, full-service companies.
When CROs focus on a particular industry like pharmaceuticals, biotech, medical device, foundations, and the government, they may niche down to focus on only a few functions within an industry. For instance, within the pharmaceutical industry, a CRO might specialize in cardiovascular disease, metabolic disorders infectious disease central nervous system (CNS), or oncology.
A full-service CRO, on the other hand, may select a site, enroll patients, and work to get approval from government regulatory agencies that oversee medications. In the US, they would take care of all the regulatory filing for the Food and Drug Administration. In Europe, they would take care of all the regulatory filing for the European Medicines Agency.
- Responsibility:
Although an organization might transfer all its clinical trial functions to a CRO, the sponsor is still responsible for the integrity of the data collected. It is up to the sponsor to verify all facts and to review the research reports to see that the best practices were followed in the clinical trial, practices that were in line with good science.
- Services:
CRO services may include project management, database design and build, data entry and validation, clinical trial data management, and medicine and disease coding. They may also cover quality and metric reporting, statistical analysis plans and reports, validation programming, safety and efficacy summaries, and the final study report.
Market Size
It’s a mistake to assume that there are hundreds of thousands of CROs across the world. This is far from the case. In fact, there are probably only a little over 1,000. This small number is because the industry is fragmented and because the work is so highly technical and specialized that it is difficult to find qualified specialists and set up the perfect facilities for a CRO. As a consequence of this exclusivity, the top companies earn billions and the CRO market itself is estimated to be worth over $20 billion.