HIV and PMTCT factsheet Nepal : High yield
Epidemiology
- First reported human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in Nepal in 1988
- Individuals infected with HIV-16,262 ((NCASC; August 2010 data).
- The most recent population based estimates (NCASC, 2009) – 63,528 adults and children
- Estimated prevalence of 0.39% in the adult population.
- During 2009, an estimated 4,701 adults and children died from Acquired Immune Deficiency (AIDS) related causes.
- Almost 29% of all people living with HIV (PLHIV) in Nepal are women. Among women, 90% of
- reported cases are of childbearing age (15-49 years age group).
Most At-Risk Populations
Nepal is described as having a “concentrated” HIV epidemic, where the estimated prevalence of
HIV infection in identified most at-risk populations (MARPs) – e.g. injecting drug users (IDUs)–
consistently exceeds 5%.
Recent estimates are that 29% of all infections occur among seasonal labour migrants, 5% among
clients of sex workers, and 28% among “low risk females” (NCASC, 2009)
HIV Infection in Women and Children
Mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) is by far the largest source of HIV infection in children in
Nepal.
The HIV seroprevalence rate among pregnant women is estimated to be 0.2%.
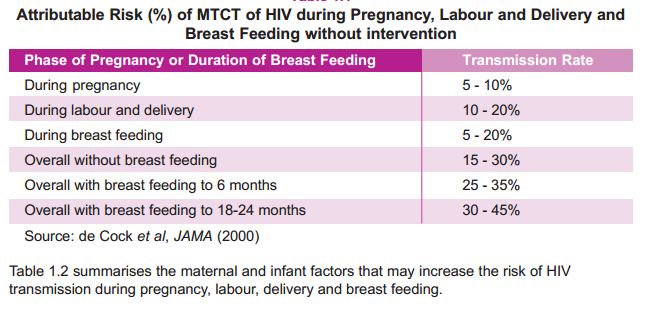
Based on this estimate, 1,228 (0.2%) of the 798,174 pregnancies each year may be expected to occur in HIV positive women. Based on an assumed vertical transmission rate of 25-45%, the annual birth
cohort of potentially infected newborns would be 307-552.
It is estimated that there are 3,544 children living with HIV in Nepal. Of these, only 1,037 have been
reported (NCASC, August 2010).
High Yield Facts-
1. PMTCT service started in Feb 2005 and now has 21 PMTCT sites.
2. Diagnostic test of choice for HIV in children <18 months- DNA PCR
3. HIV antibody testing ELISA- 100% sensitive 99% specific
4.Two positive Antibody test needed to confirm the diagnosis.
5. Pneumocystis is commoner in younger age group children and LIP in more than 2 yrs children.
Differences in pediatric and adult HIV
- Overall progression is more rapid in children
- Immune system is immature with higher CD4+ counts
- Recurrent invasive bacterial infections more common
- Disseminated CMV, candida, herpes, varicella are more common in children
- LIP occurs exclusively in children
- CNS infections are more common
- Peripheral neuropathy, myopathy and Kaposi sarcoma are rare in children.
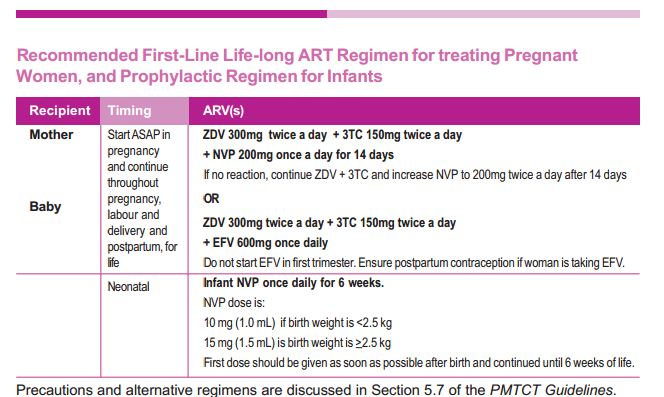
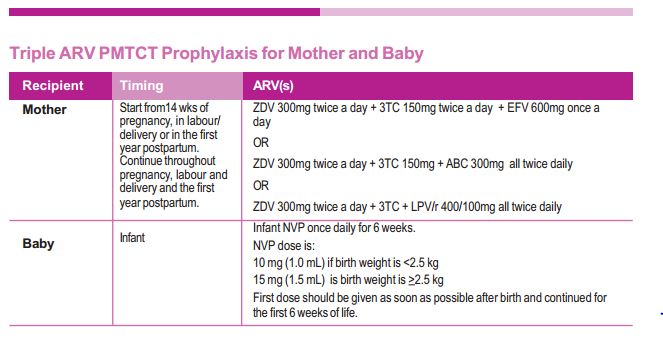
Guidelines- PMTCT
Must read Guidelines – Download PMTCT guidelines and Management of HIV and AIDS in children in Nepal 2011.