MBBS/BDS Entrance Exam Curriculum by MOE (Nepal)
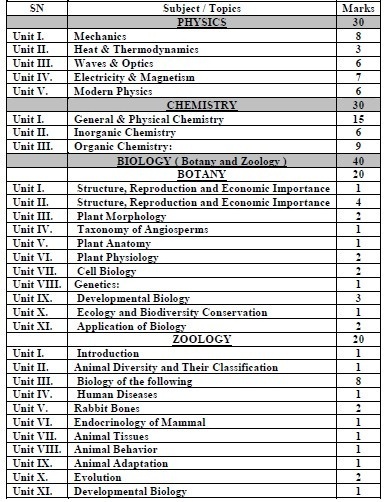

PHYSICS
Group (A) Mechanics
- General concept of physical quantities, Vector algebra
- Laws of Motion, Application of Newton’s laws, Work, Energy and Power, Projectile motion
- Circular Motion, Motion round a banked track and in vertical circle
- Newton’s law of gravitation, Variation of ‘g’ with altitude and depth, Satellites, Gravitational potential energy, Escape velocity, Black holes
- Elasticity, Hooke’s law, Young modulus, Bulk modulus, Elastic potential energy
- Oscillatory motion, Simple harmonic motions, Damped oscillation, Forced oscillation and resonance
Group (B) Heat and Thermodynamics
- Concept of heat and temperature, Expansion of solid and liquid, Specific heat capacity, specific heat capacity of solid, Specific latent heat of fusion and its measurements
- Thermal conductivity and its determination by Searle’s method, Black body radiation, Stefan-Boltzmann law
- Thermodynamic systems, First law of thermodynamics, Heat capacities of ideal gas at constant pressure and constant volume and relation between them, Isothermal and adiabatic processes for an ideal gas, Second law of thermodynamics
Group (C) Waves and Optics
- Reflection & Refraction of light, Refractive index, Lateral shift, Minimum deviation through prism, Relation between angle of prism, minimum deviation and refractive index, Lenses, Combination of thin lenses in contact
- Dispersion, Dispersive power, Achromatic lenses, Scattering of light, blue color of the sky
- Optical instruments, Angular magnification, Compound microscope, Astronomical Telescope
- Longitudinal and transverse waves, Progressive and stationary waves, Velocity of sound in medium, Laplace’s correction, Stationary waves in closed and open pipes, Harmonics and overtones in closed and open organ pipes, Resonance tube experiment, Laws of transverse vibration of a stretched string
- Characteristics of sound, Intensity, loudness, quality and pitch, Beats, Doppler’s effect, Infrasonic and ultrasonic waves
- Physical optics, Wave theory of light, Interference, Diffraction and Polarization, Coherent sources, Young’s double slit experiment, Diffraction grating, Brewster’s law
Group (D) Electricity and Magnetism
- Coulomb’s law – Force due to point charges, Gauss law and its applications: Field of a charged sphere, Line charge; Potential due to a point charge, Electron volt, Capacitance of a capacitor, Parallel plate capacitor, Combination of capacitors
- Electric Currents, Drift velocity and its relation with current, Ohmic and Non-Ohmic resistance, Resistances in series and parallel, Electromotive force of a source, Internal resistance, Work and power in electrical circuits, Kirchhoff’s laws, Wheatstone Bridge circuit, Meter Bridge, Potentiometer
- Magnetic field lines and magnetic flux, Force on moving charge, Force on conductor, Force and torque on rectangular coil, Ampere’s law and its application to i) a long straight conductor ii) a straight solenoid, Faraday’s laws of electromagnetic induction, Lenz’s law
- AC through resistor, capacitor and inductor, Series circuits containing combination of resistor, capacitor and inductor, Series resonance, Choke coil
Group (E) Modern Physics
- Electrons: Millikan’s oil drop experiment, Cathode rays and their properties; Motion of electron beam in electric and magnetic fields, Thomson’s experiment to determine specific charge of electrons
- Quantum nature of radiation, Einstein’s photoelectric equation, Stopping potential
- Intrinsic and extrinsic semi-conductors, P-N Junction diode, Forward and reverse bias, Rectification, Zener diode
- Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom, Spectral series, Excitation and ionization potentials, Energy level, de Broglie Theory, Duality, Uncertainly principle
- Lasers: Properties and uses, X-rays: Production, properties and uses
- Basic concepts of nucleus, Mass Defect and amu, Einstein’s mass-energy relation, Binding energy, Fission and fusion, Alpha-particles, Beta-particles, Gamma rays, Laws of radioactive disintegration, Half-life and decay constant, Health hazards and safety precautions
CHEMISTRY
Group (A) GENERAL AND PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
Part (1) Language of Chemistry and Chemical Arithmetic
I. Language of Chemistry (Review)
- Chemical equations, their significances and limitations.
- Balancing chemical equations by: Hit and trail method and Partial equation method
- Types of chemical reaction
- Chemical Arithmetic
- Dalton’s atomic theory and Laws of Stoichemistry: Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory, Law of conservation of mass, Law of constant proportions, Law of multiple proportion, Law of reciprocal proportion, Law of gaseous volumes, Chemical calculations based on stoichiometry
- Atomic Mass and Molecular Mass:
- Definition of atomic mass and molecular mass
- Mole concept
- Mole in term of mass, volume number and ions
- Calculation based on mole concept
- Empirical, Molecular Formula and Limiting Reactants:
- Percentage compositions
- Derivation of empirical and molecular formula from percentage composition
- Chemical calculation based on following chemical equation
- Limiting reactants
- Mass-mass relationship
- Volume- volume relationship
- Mass volume relationship
- (Solving related numerical problems)
- Avogadro’s Hypothesis and its applications:
- Development of Avogadro’s hypothesis
- Definition of Avogadro’s hypothesis
- Application of Avogadro’s hypothesis
- Deduction of atomicity of elementary gas
- Deduction of relationship between molecular mass and vapour density
- Deduction of molar volume of gases
- Deduction of molecular formula from its volumetric composition
- (Solving related numerical problems)
- Equivalent Masses:
- Concept of equivalent mass
- Equivalent weight of elements and compounds (Salt, acid, base, oxidizing agents, reducing agents)
- Gram equivalent weight (GEW)
- Relation between equivalent weight, valency and atomic weight
- Determination of equivalent weight of metal by
- Hydrogen displacement method
- Oxide formation method
- (Solving related numerical problems)
Part (2) States of Matter
I. Gaseous State:
- Boyle’s law
- Charles law and Kelvin scale of temperature
- Application of Charles law and Boyle’s law
- Combined gas law, ideal gas equation and universal gas constant
- Dalton’s law of partial pressure
- Mathematical derivation of Dalton’s law and their applications
- Graham’s law of diffusion and its applications
- Kinetic model of gas and its postulates
- Ideal and real gases
- Deviation of gas from ideal behavior
- (Solving related numerical problems)
II. Liquid State:
- Physical properties of liquid
- Evaporation and condensation
- Vapour pressure of liquid and boiling
- Surface tension
- Viscosity
- Solution and solubility:
- Equilibrium in saturated solution
- Solubility and solubility curve and its applications.
- (Solving related numerical problems)
III. Solid State:
- Crystalline and amorphous solids
- Water of crystallization
- Efflorescence
- Deliquesces
- Hygroscopic
- Seven types of crystal system
- Simple cubic, face centered and body centered
Part (3) Atomic structure and Electronic theory of valency
- Discovery of fundamental particles of atom (electron, proton and neutron)
- Concept of atomic number, mass number, fractional atomic mass, isotopes, isobars
- Rutherford’s α ray scattering experiment and nuclear model of atom; limitation
- Bohr’s model of atom and explanation of hydrogen spectra
- Limitation of Bohr’s model of atom
- Elementary idea of quantum mechanical model
- Dual nature of electron (de-Broglie equation)
- Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle
- Probability concept
- Shape of atomic orbital (s and p orbitals only)
- Quantum numbers
- Pauli’s exclustion principle
- Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity
- Aufbau principle and Bohr Bury rule
- Electronic configuration of the atoms and ions (Z= 1 to 30)
- Basic assumption of electronic theory of valency
- Octet rule
- Ionic bonds, ionic compounds and characteristics of ionic compounds. Lewis symbol to represent the formation of ionic compounds
- Covalent bonds, covalent compounds and characteristics of covalent compounds-Lewis structure of some typical covalent compounds
- Co-ordinate covalent bonds. Lewis structures of some typical co-ordinate covalent compounds
- Exception of the octet rule
- Partial ionic characters of covalent compounds. Non-polar and polar covalent molecules
Part (4) Periodic Classification of Elements
- Introduction
- Mendeleev’s periodic law and periodic table
- Anamolies of Mendeleev’s periodic table
- Modern periodic law, and modern periodic table
- Advantage of modern periodic table
- Division of physical properties: valency, atomic radii, ionic radii ionization energy, electron affinity and electronegativity (general trends only)
Part (5) Oxidation and Reduction
- Classical concept of oxidation and reduction
- Electronic interpretation of oxidation and reduction
- Oxidation number and rules for the assignment of oxidation number
- Differentiate between oxidation number and valency
- Oxidising and reducing agent
- Redox reaction
- Balance redox reactions by:
Oxidation number method
Ion-eletron method
Group (B) INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Part (1) Non-metals
- Water
- Structure
- Solvent property of water
- Heavy water and uses
- Uses
- Nitrogen and Its compounds
- Ammonia
- Manufacture by Haber’s synthesis method
- Physical properties, chemical properties and uses
- Carbon
- Allotropes of carbon including fullerenes
- Sulphur
- Hydrogen Sulphide: (Laboratory methods and Kipp’s apparatus), properties and uses of
- Sulphurdioxide: Laboratory preparation, preparation and uses
- Sulphuric acid: Manufacture by contact process, properties and uses
- Environmental Pollution:
- Air pollution, photochemical smog
- Acid rain, water pollution
- Green house effect
- Characteristics of metals, non-metals and metalloids
- Minerals and ores
- Important minerals deposit in Nepal
- Different process involved in metallurgical process
- Concentration
- Calcinations and roasting
- Smelting
- Carbon reduction process
- Thermite process
- Electrochemical reduction
- Refining of metals: poling, electro-refinement etc.
Part (2) Metal and Metallurgical Principles
Group (C) ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Part (1) Introduction ot Organic Chemistry
I. Fundamental Principles:
- Definition of organic chemistry and organic compounds
- Origin of organic compounds (vital force theory)
- Reasons for the separate study of organic compounds
- Tetra covalency and catenation property of carbon
- Classification of organic compounds
- Functional groups and homologous series
- Meanings of empirical formula, molecular formula, structural formula and contracted formula
- Qualitative analysis of organic compounds. (detection of N, S and halogens by Lassaegne’s test)
II. Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
- Common names
- IUPAC system and IUPAC rules of naming hydrocarbons, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, carboxylic acid, amines, ester, acid derivative halogen derivatives, nitriles etc.)
III. Structure Isomerism in Organic Compounds
- Definition of structure isomerism
- Types of structure isomerism: chain isomerism, position, isomerism, functional isomerism and metamerism
IV. Preliminary Idea of Reaction Mechanism
- Concept of hemolytic and heterolytic fission
- Electrophile, nucleophiles and free-radicals
- Inductive effect, +I and –I effect
- Hybridization and concept of sigma and pi bond
- Valence shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory
- Prediction of molecular geometry (Shape of molecules) on the basis of VSEPR and hybridization.(BeF2, BF3, NH3, H2O, CH4, H2O, C2H2 C2H4 H2S)
Part (2) Chemical Bonding and Shape of Molecules
Part (3) Volumetric Analysis
- Different ways of expressing the concentration of solutions.
- Molarity
- Normality
- Molality
- Gram/ Litre
- Percentage
- Titration:
- Acid-base titration
- Redox titration
- Primary standard substances, primary standard solution, secondary standard solution, end point, equivalence point, neutral point, indicators.
- Derivation of normality equation
- Relation between normality and molarity
- Selection of indicators in acid-base titration and PH curve
- Solving related numerical problems
Part (4) Ionic Equilibrium
- Introduction
- Ionization of weak electrolyte (Ostwald’s dilution law)
- Degree of ionization and ionization constant
- Strength of acid and base in term of Ka, Kb and pKa, pKb values
- Acid-base concept
- Arrhenius concept of acids and bases
- Bronsted lowrry concept concept of acids and bases
- Lewis concept of acids and bases.
- Ionization of water, pH and pH scale.
- Hydrolysis of salts. (qualitative concept)
- Solubility product principle and its application
- Common ion effects and its application
- Application of solubility product principle in qualitative analysis
- Buffer Solution
- (Solving numerical problems related with solubility, solubility product, pH and pOH)
Part (5) Alcohols and Phenols
I. Alcohols
- i. Introduction, classification, nomenclature and isomerism
- ii. Distinction of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol by Victor Mayer’s Method
- iii. Preparation of monohydric alcohols form
- Haloalkane
- Grignard’s reagents using aldehydes
- Primary amines
- Ester
iv. Industrial preparation ethanol form:
- Oxoprocess
- Fermentation of sugar
- Hydroboration of ethane
- Physical properties monohydric alcohols
vi. Chemical properties of monohydric alcohols
- Reaction with HX. PX3, PCl5SOCl2
- Action with reactive metals like Na, K, Li
- Esterification process
- Dehydration of alcohols
- Oxidation of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohol with oxidizing agents.
- Reduction of alcohols (Catalytic dehydrogenation)
- Laboratory test of ethanol
- Absolute alcohol, methylated spirit, rectified spirit; alcoholic beverage.
- Preparation and uses of ethan- 1.2. diol (glycol)
- Peparation and uses of Propan- 1, 2, 3 triol (glycerol)
II. Phenols
- Introduction to phenol
ii. Preparation of phenol from
- Chlorobenzene
- Diazonium salt and
- Benzene sulphonic acid
- Physical properties of phenol
- Chemical properties
- Acidic nature of phenol
- Action with PCl5, PX5, NH3, Zn, Na benzene diazonium chloride and phthalic anhydride
- Acylation reaction, Kolbe’s reaction, Reimer Tiemann’s reaction
- Electrophilic substitution: halogenations, nitration, sulphonation bromination and Friedal Craft’s alkylation
- Laboratory test of phenol
- Uses of phenol
Part (6) Aldehydes and Ketones
I. Aliphatic Aldehydes and Ketones
- Introduction, structure of carbonyl group, nomenclature and isomerism in carbonyl compound
ii. Preparation of aldehydes and ketones from
- Dehydrogenation and oxidation of alcohol
- Ozonolysis of alkenes
- Acid chloride
- Gem dihaloalkane
- Catalytic distillation of fatty acid
- Distillation of salt of fatty acid
- Catalytic hydration of alkynes
iii. Physical properties
iv. Chemical properties
- Addition reaction: addition of H2, HCN, NaHSO3 and Grignard’s reagents
- Action with ammonia derivatives; NH2OH, NH2- NH2, phenyl hydrazine, semicarbazides and 2,4-DNP
- Reduction properties of aldehydes
- Oxidation with Tollen’s reagent, Fehling’s solution
- Aldol of condensation reaction; clemennson’s reduction Wolf-Kischner reduction, Action with PCl5, action with ammonia, action with phenol, formalin and its uses.
II.Aromatic Aldehydes and Ketones
- Preparation of benzaldehyde from toluene
ii. Properties of benzaldehyde
iii. Important reaction benzaldehyde different from aliphatic aldehydes:
- Perkin condensation
- Benzoin condensation
- Electrophilic substitution reaction
- Canninzaro’s reaction
- Preparation of acetophenone by Friedal Craft’s acylation
Part (7) Molecules of Life
- Carbohydrates: definition, classification of carbohydrates, various examples of carbohydrate of different class. Structure and glucose and fructose, function of carbohydrates, sugar and non-sugar.
- Protein: definition, amino acid, essential and non-essential aminoacids, peptide linkage, hydrolysis of aminoacids, denaturation of protein, zwitter ions, functions of aminoacids.
- Nucleic acid: definition, basic components of nucleic acid; double helix, difference between RNA and DNA; biological function of nucleic acid
- Lipid: definition, fatty acids, fat as ester of fatty acid and difference between fats and oils, function of lipid
- Enzymes and their functions.
Part (8) Chemistry in Service to Mankind
- Polymer: definition, natural and synthetic polymers, homopolymers and co-polymer preparation of some polymers; PVC polyethene polystyreno Teflon, Nylon-66, Bakelite and their uses
- Dyes and drugs : definition, natural and synthetic dyes, names and structure of some common drug, drug addiction
- Fertilizer: definition, chemical and organic fertilizers, nitrogen fertilizer, phosphatic fertilizer; fertilizer as pollution
- Pesticides: insecticides, herbicides, weedicides and fungicides (examples and their uses).
BIOLOGY
Group (A) BOTANY
Part (1) Introduction to biology
- Scope of biology, field of bilogy, life processes
- Biomolecules (macromolecules & micromolecules)
- Taxonomy
- Two kingdom and five kingdom system of classification
- Binomial/trinomial nomenclature
- Structure, types and economic importance of virus, bacteria and lichens
Part (2) Biodiversity
- Structure and life cycle of Spirogyra, Blue green algae, Marchantia, Dryopteris, Cycas and Pinus
- Floral diversity of Nepal
- Forest conservation
- Types of forest of Nepal & their management
Part (3) Morphology
- Distributation, habitat, habit, root, stem, leaf, flower, fruit and seeds of families – Brassicaceae, Solanaceae, Papilionoidae, Asteraceae and Poaceae
- Taxonomy and economic importance of families given above
Part (4) Cytogenetics
- Cytology
- Introduction, structure and functions of prokaryotic and eukarotic cells
- Cell division – amitosis, mitosis and meiosis
- Genetics
- Introduction, Mendelism, Genetic material ( DNA & RNA), Mutation
Part (5) Anatomy and physiology
- Anatomy
- Types of tissues (meristematic, permanent and special types of tissues)
- Internal structure of dicot and monocot leaf, stem and root
- Physiology
- Water relation – osmois, diffusion, anscent of sap and transpiration
- Photosynthesis – mechanism and factors
- Respiration – anaerobic and aerobic
- Hormones – physilolgical effects of auxins, gibberllin, cytokinin and abscisic acid
Part (6) Ecology
- Introduction, ecosystem (pond & grassland)
- Biogeochemical cycle – nitrogen and carbon
- Ecological imbalance and its consequences – green house effects, acid rain , depletion of ozone layer
Part (7) Developmental biology
- Reproduction – vegetative propogation, sporogenesis, gametogenisis
- Pollination, fertilization
Part (8) Application of biology
- Introduction to biotechnology, tissue culture, concept of breeding technique, disease resistant plants, biofertilizer, perticides
- Genetic engineering and its application
- Fermentation technology – alcoholic, antibiotics, organic acids
Group (B) ZOOLOGY
Part (1) Biodiversity
- Kingdom – Protista – general characters and classification of phylum – Protozoa upto classes with eamples
- Paramecium caudatum – distributation, habitat, habit, structure and reproduction
- Kingdom – Animalia – general characters and classification of phyla – Porifera, Cnidaria, Platyhelminthes, Nemathelminthes Annelida, Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata and Chordata upto clases with examples.
- Faunal diversity of Nepal
Part (2) Anatomy and type study
- Animal tissues – epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous, their structure, types, location and function
- Earthworm and forg – distrubutation, habitat, habit, external feature, digestive system, respiratory system, excretory system, circulatory system, nervous system, reproductive system and economic importance.
Part (3) Human/rabbit physiology
- Digestive system – alimentary canal, associated glands and physiology of digestion
- Respiratory system – lungs, mechanism of breathing, physiology of respiration
- Escretory system – kidney, urine formation, osmoregulation and homoeostaisis
- Circulatory system – heart, working of heart, blood groups, blood prssure, arterial and venous system
- Reproductive system – male and female reproductive orgnas, associated glands, memtrual cycle.
- Nervous system – CNS (Brain and spinal cord), PNS and ANS
- Endocrine system – pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, pancreas
Part (4) Developmental biology
- Gametogenesis – spermatogeneris, oogeneris
- Fertilization, cleavage
- Morulation, blastucation, gastrulation and neurulation
- Coelom formation
- Fate of three primary germinal layers
Part (5) Origin and evolution
- Evolution – inorganic, organic
- Inorganic evolution – originof life, Oparin – Haldane’s theory, Miller – Urey experiment
- Organic evolution – evidences of organic evolution
- Lamarchism, Darwinism, Neo-Darwinism
- Human evolution
Part (6) Environmental relations
- Environmental pollution – air and water, sources, effects and control measures
- Migratory behavior of fishes and birds
- Adaptation in amimals – aquatic terrestrial, aerial
- Conservaton of wild life, wild life reserves, national parks, natural resources
- Protection of the earth – human responsibility
- Human population growth – consequences of over population, control measures
Part (7) Diseases
- Smoking, alcoholism, drug abuse, symptoms impact on health and society, rehabilitation, control
- Malaria, ascariaris, typhoid, tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS, mode of trammission, symptoms, control
- Cancer – types, symptoms, control
Part (8) Medical technology and economic zoology
- Test tube baby
- Amniocentesis
- Tissue and organ transplantation – skin, cornea, kidney, blood transfussion
- Animal breeding
- Fish farming, poultry farming
- Antibiotics and vaccines
Marking Scheme:





64 Comments
no i didnt get passed in iom …actually my main question is that what is a maximum marks we need to get in moe for the b pharma????
hey admin ,i had gave xam in iom but i didnt got a chance to read …i had also filled the form of moe…actually i want to read b pharma ..but i fill the form of mbbs bcoz i have been told that if we got nice mark then we can get a chacnce to read in tu affiliated colz …so my main question is that how many mark we need to get to read in moe affiliated colz…and plz tell me what is the fee for b pharma in tu affiliated colz
Alina,
You can apply in TU affiliated college if you pass IOM entrance. About the college fee, you will need to find it for yourself, because each year fees are being revised and we have not been able to get updates on B Pharma
hi sir,
my question is that when the next entrance exam for mbbs is going to held. and how many times the exam is held in a year?
plz reply me as soon as possible.
MOE scholarship application form submission is on the final dates upto 2068 Asoj 10, as late date. For more info visit http://moe.gov.np
Next entrance will be held 6 months later
respcted sir,wat is the last date of submiting the form of moe helding in month of kartik 26 n 2 fal under janjati quota what r the criteria?????iz only transcrpt of +2 is needed while form submision?????
MOE scholarship application form submission is on the final dates upto 2068 Asoj 10, as late date. For more info visit http://moe.gov.np
To get Janajati Quota , you need recommendation from Janajati office that becomes your legal document.
dear sir,
i have keen interest in chemistry.but my parents force me to study mbbs .they say believe that here is no any scope of chemistry in nepal.so plz tell me what should i do in this situation
If you have a keen interest in Chemistry, search for the options in the field. Secure where you can go for further studies and what you will do in future.
Convince your parents with your plan and eventually they will accept your wish.
dear sir,
I’m a H.A. Students affilated by CTEVT and i have also pre-request course. I’m also janajati. So want to ask you 1 question. Is syllabus of H.A+pre-request course sufficient for the medical entrance in nepal or not ? If sufficient, whats the possibility of getting scholarship…
dear sir,
When will moe conduct da scholarship xam for bangladesh n in which clz of banglades does it send da deservin studnt?plz reply soon..thnx in advance…
sir
i have something serious about the entrance exam
as there are quotas different for different people from different localities of our country Nepal. but is it necessary to give quotas for getting scholarship exam.i mean to say that cant it be possible that there would be the free competition as it is in IOM. If it is available in IOM then why cant in MOE however the quotas system can help the student from remote places to succeed in entrance.If it is necessary to provide quotas then it should be only to those candidates who had passed their +2 courses from remote places otherwise it brings discrimination between two students. Due to the quota many student are facing problems like a talent students gets 90 marks n cant get seat in Moe but in the other side due o the quota a student scoring only 70 become legible for Moe scholarship.If there occur same prblm for many years then we can be sure that the day is not far that the person who is duffer becomes doctor and one who is genius will have to lose the dream of being doctor and in Nepal in near future everyone will be scared of DOCTOR.
Exactly Neeraj,
We ourselves are against the quota system on the basis of caste and origin. Quota should be provided to those who are needy and come from remote for whom free competition would be unfair. Many people have taken advantage of the quota system.
Else for all others, there should be free competition so that the Best of the Best can get into this field and hence improve the quality of doctors here.
Respected Sir,
I have a few questions to be asked. Sir, I want to read BDS under scholarship but is there good scope of BDS in Nepal? Also what are the ways to get scholarship to read BDS? How to apply in colleges as well? Sir plz reply soon.
BDS is a good subject. You can get an MD degree or MDS after that.
BDS scholarship is offered by MOE, Nepal as well as TUTH and Dharan.
KDC, NDC etc provide private enrollment to Dental students.
Sir, to read BDS under scholarship, Does MOE give full or partial scholarship or some percent only? plz reply soon.
MOE provides you full scholarship for BDS.
Dear sir i had pass the pcl level of lab technology first yr n second yr but third yr is running still now.so shall i allow to give mbbs entrance?
Hello Binamrata,
You will be eligible for MBBS course only after completing the 3 year course of PCL in Medical Lab Technology and then completing a “Refresher course” of Science conducted by HSEB (Higher Secondary Education Board).
Dear administrator,
What sort of technics we have to apply during study to get listed our name in MOE. Only reading and reading is enough for it?
Of Course Sonam, Reading is simply not enough but reading is very necessary.
You have to go through high yield contents like Books with probable questions, past questions, quick reviews, high yields etc.
More over you have to attend preparation classes and exams can be very helpful.
See if you fit into Criteria like Janajati, Adibasi, Female,etc. Fighting through quota is much easier than open competition.
Hello sir!My qustion for u is
I failed 2 subjects in class 11 n in 12 too…So lost 1yr..I gave the 12 xam now…so can i join MBBS after i passed the xam??
Hello Najmila,
I’m not quite sure about this issue. If you fulfill the percentage criteria for MOE exam, you will probably be eligible for exam.
Else there is Private KU exam, you can always get enrolled in MBBS if you pass and qualify KUMET.
hi,sir my permanent address is tanahu district and my citizenship is also of tanahu district.i gave my slc exam from chitwan and my slc certificate is also of chitwan district.is it necessary to have slc certificate and citizenship must be of same district to give exam of mbbs in quta?
No, you are eligible to apply for the quota if your schooling zone fulfills the criteria.
hi sir,
my question is that “the students who failed in 11 board exams n had jus given the conpart exms are they allowed to apply for the given entrance exms of this year…n my next que is r we allowed to give entrance exm of bds of india from MOE..plz sir reply as soon as possible..
Hello Liza
Eligibility criteria: Must have passed Plus 2 or I.Sc. with 50% marks in Physics, Chemistry, Biology.
You also need to submit this document along with form:
10+2/I.Sc. Passed Transcript or Equivalent certificate
There is no scholarship scheme for BDS in India through MOE of Nepal. The scholarship seats are made available only by the Indian Embassy.
MOE ma name nikalna paisa gus khuauchan re ho ra?
According to Mahes ” To get listed in MOE scholarship do people bribe authorities?”
Mahes,
We are not sure of such claims but such claims have been made frequently. Students have claimed that there are People who scam students by luring them. You must always be aware of them. They are said to be seen near exam centres and MOE, looking for victims.
Dear admin, i am a poor muslim and madhesi student from Bara district. I studied in village upto 8 class in a gov.school and after that i was brought to kathmandu by my father’s master and i worked and passed slc frm a semi-gov school. Then i just appeared 12 science with full scholorship n wish to study mbbs but i cant afford. To fall in reservation is it impt to pass slc from a gov school? Pls help me.
Hello Samsad,
25% of the seat reservation is for poor of which:
a) 20% is for Madhesi
b) 2% is for Muslim
According to MOE, anyone who passed SLC from any school within Nepal can fall in reservation under the specified criteria (Poor,Disabled,etc.) if there is no person passing SLC from government school available.
thank you sir/mam, and will you please make me clear about what documents, I need to present and how will I get them?
You’ll need certificate that will prove your quota from respected office. Eg, Janajati Certificate from Janajati office etc.
You should consult MOE for details on the subject.
dear sir
the old question collection for MBBS entrance exam of Patan Hospital is availabbe or not? If available,from where we can buy this book?
Hello Srijana,
You should really check it out at “Namaste” Shop in front of NAME, Putalisadak.
hello sir ,
I am a A level students. so want to ask you 1 question . Is syllabus of A levels sufficient for the medical entrance in Nepal . whats the possibility of getting scholarship . And do you know some A levels students doing MBBS in NEpal..
really like to hear from you soon ..
tc
Hello manish,
There are A level students studying MBBS in Nepal and I know few of them.
The syllabus for A level as well as 10+2 or I.Sc. would not be adequate for the entrance exam. Hence, you need to join a bridge course for Entrance exam preparation in institutions like NAME, Orbit, Sachdeva , NINE etc.
The possibility of getting scholarship depends on the effort you put in the preparation as well as sheer luck. However, there are numbers of seats allocated for various quotas in MOE which increases the chance of securing scholarship.
dear admin, as i am almost sure not to take entrance preparation classes for the entrance examination in the reputed institutes of Kathmandu due to my own personal problems, if i prepare on my own……..do i stand a chance to get my name on the list???? if yes, what do i need to do???please help me out!!! 🙁
You dont need to take Preparation Classes for MBBS entrance if you can sit home and study for it.
All you have to know is the course. Try to follow the books used in NAME,Sachdeva,Orbit etc. and you can also appear for model exams without being enrolled.
And make sure you go through the past questions as well.
Can you tell me the sort of books (name of publication or writer) which will really help to get through moe exams. Most of the objective books seems very vast for the exams.
Always go for fast Review books and crash course books.
Books containing high yield questions and past questions will be equally helpful.
how to study the chemistry basically inorganic and organic for the medical entrance?i dont have any idea and i feel it very difficult…could u help me
Manoj,
For the MOE entrance exam, all you need is the things you read in your Intermediate ( +2) level. Go for the preparation books if you are short of time and solve the high yeild questions as questions do repeat.Go through the past questions to know what sort of questions can be asked.
Inorganic and Organic section- We have mentioned the syllabus above.
Sir is there also Reservation Seat for Remote area’s Student? But sir i passed +2 level from Kathmandu and slc from remote area…
Hello Akhanda,
You may be elligible for ther reservation seat if:
a. The school is a Government School
b. If your home/address is a remote location
Sasshee,
Reservation system is there in MOE for Scholarship seats-
25% quota is there for poor students but he/she must be Madheshi, Muslim or family of Martyr or missing people during the war.
Janajati 25% quota
Female gets 33% quota
dalit 9%
Disabled 2%
If you fall in any criteria or 2 of these criteria you will have a higher chance of getting a scholarship.
Prepare for next exam seriously and you may get through.
Try out Indian embassy, Bangladesh and Japanese Embassy scholarship test.
Hope this helps, any questions feel free to ask us.
as my father was killed by maoist during their 12 year war ..he was a permanent teacher in dolakha..the people who were killed during war were declared as martyrs…but have not given any paper so that we can say him martyrs..can i get an exams in quota?i have all papers and he is in the government list that he was killed and declared martyrs..
i will be very happy if u humbly reply my comment
thank you
Bidur,
Ministry of Education has declared quota for Martyr of Revolution.
But We do not have a clear idea on the topic.
It would be best if you once consult MOE regarding the matter- are you eligible for the quota,what all documents are required for the quota etc.
You can have a clear idea then.
Sorry, we couldn’t help you much. We will update you if we find the answer.
dear sir,my question to u is,whats the criteria of getting scholarships as my parents can’t afford for my studies.isn’t there any criteria of giving scholarships to the poor studets?I gave an exam in MOE and i got 71 marks.I was unable to take out my name in scholarship.So,i am confused what to do as my parents can’t afford me to study MBBS but my aim is to study MBBS.So,can u give me a good suggestion.
dear sir, how to join MBBS in you’r contry
Hi Sujatha, looks like you are from India. So, you have to join a bridge course preparation for entrance examinations or you can prepare on your own. Then all you have to do is appear exams and follow the procedures onward. There are special seats for foreign students also.
For Students from SAARC and non SAARC countries, Direct admission facility is there after an interview.
You need to complete your Intermediate or +2 levels. Then you can contact the colleges you like via websites or phone.
If you have any doubts, you can ask freely.
Comments are closed.