Antibiotic Resistance and Newer antibiotics- An overview
Drug Resistance
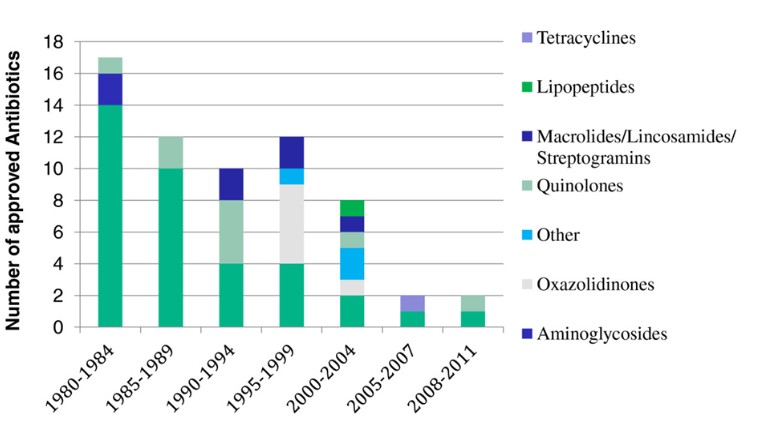
‘Innovation gap’ is the expression that has been used to describe the lack of novel structural classes introduced to the antibacterial armamentarium since 1962. Since 2000 –Only 3 new classes of antibiotics have been introduced to the market for human use , 1 limited to topical use
Recently, IDSA supported a proGram, called “the ′10 × ′20′ initiative”, to develop ten new systemic antibacterial drugs within 2020 through the discovery of new drug classes, as well as to find possible new molecules from already existing classes of antibiotics.
How the antibiotics have failed
Recently the arrival of the Vancomycin resistant strains like- VRSA, VRE have raised a anxious concern in the critical care physicians. Many hospitals have created stewardship programs to prevent misuse of antibiotics. Many have deferred the empirical use of Vancomycin in Febrile neutropenia patients if MRSA is less likely.
The drug active against VRSA are-
- Linezolid
- Telavancin
However, Recommendations for the treatment of carriage of VRSA do not exist.
Ceftaroline considered ‘fifth-generation’ cephalosporin. Newest cephalosporin with anti-MRSA activity that obtained FDA approval in October 2010. Indicated in acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections, and community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. Spectrum- –MSSA as well as MRSA, Strep. Pyogenes, agalactiae, and pneumoniae, hVISA and VRSA, Gram-negative -ceftazidime-susceptible E. coli and Kleb. pneumoniae, and β-lactamase-positive and negative Haemophilus influenzae. It has a synergistic effect when combined with amikacin, tazobactam, meropenem and aztreonam and has low potential for resistance development and the favorable safety and tolerability profile in clinical trials.
Carbapenems have widest spectrum of antibacterial activity of all the beta-lactams and have excellent coverage- Gram – and Gram + aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. These are bactericidal agents that bind to the PBPs inhibiting the bacterial cell wall synthesis.Less resistance than other beta-lactams because of their stability to hydrolysis by many extended-spectrum chromosomal and plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases, including AmpC and extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs).
The Group III carbapenems- Razupenem and Tomopenem are also active against the Pseudomonas , Acinetobacter baumanni and MRSA strains.
Tigecycline, a novel tetracycline is approved for use and is mainly effective againt the Acinetobacter baumanni the pan-drug resistant forms. However it is contraindicated for use in <8 yrs age group due to teeth staining and cartilage toxicity. Coverage spectrum of Tigecycline- against gram-negative as well as positive organisms makes it a useful drug in mixed infections. Potent activity against a number of resistant organisms including A. baumannii
- Few newer Group of antibiotics have been introduced. Most are derivatives of previously used classes.
- MRSA,VRSA,VRE, ESBL, Pseudomonas are major resistant organisms
- Against which most new antibiotics are targeted.
- Rationale use of the antibiotics is necessary because erratic use in past
- has led to rapid and extensive drug resistance