Maternal Rhesus Isoimmunization : Rh incompatibility
Alloimmunization (Isoimmunisation) is defined as the antibody response to foreign antigen derived from different individual of the same species. Rh alloimmunization refers to the development antibodies to Rh D antigen. Antibodies may be produced to Rh antigens C,c,D,E, or e but only D is strongly immunogenic.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
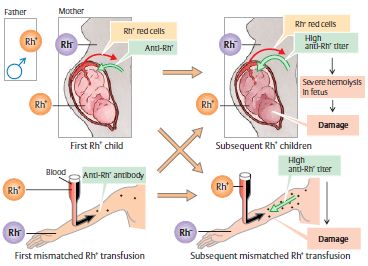
- 1st Rh+ve pregnancy: Rh negative mother bearing Rh positive fetus
- Feto-maternal bleed: Abortion, Amniocentesis, Antepartum hemorrhage, Abdominal trauma, Chorionic villous sampling, Cordocentesis, Ectopic pregnancy, External cephalic version
- Critical sensitizing volume: Atleast 0.1 ml of fetal blood enters maternal circulation. Fetal blood complete lifespan and are destroyed in RES o liberate antigen.
- Rh Sensitization: Initial maternal immune response is low levels of IgM which is unable to cross placental barrier. Pregnancy at this time is usually unaffected. Within 6 weeks to 6 months, IgG antibodies become detectable and is capable of crossing the placenta.
- 2nd Rh+ve pregnancy: IgG antibodies cross palcenta
- Immune reaction: Agglutination of fetal RBC leading to hemolysis
- Fetal effect: Hemolytic disease of newborn
Maternal Rh isoimmunization can also occur if a Rh +ve blood is transfused to Rh -ve mother.
Risk of sensitization depends upon 3 factors:
- Volume of transplacental hemorrhage
- Extent of maternal immune response
- Concurrent presence of ABO incompatibility
Incidence of Iso-immunization is only 2-16% because of following factors:
- Rh-stimulus non-responders
- Critical sensitizing volume: 0.1 ml
- Difference in immunogenicity of antigen
- ABO incompatibility: ABO incompatible fetal cells are cleared from the maternal circulation rapidly before they are trapped by the spleen (RES)
3 GRADES OF SEVERITY OF HEMOLYTICS DISEASE OF NEWBORN
- Congenital anemia of newborn (Mildest i.e. Hb>/=12 gm/dl): 50%
- Liver and Spleen enlarged (Extramedullary hematopoiesis)
- No active treatment required
- Icterus Gravis neonatarum (Moderate i.e. Hb 7-12 gm/dl): 25-30%
- Not born with Jaundice (Bilirubin Excreted through feto-maternal circulation) but develops within 24 hrs of birth. This is because, there is no feto-maternal circulation after the cord is clamped.
- When bilirubin >20mg/dl it crosses the blood brain barrier leading to Kernicterus and Encephalopathy.
- Features of Kernicterus: Loss of Moro reflex, posturing, poor feeding, inactivity, bulging of fontanelle, high-pitched shrill cry and seizures.
- Treatment: Phototherapy or Exchange transfusion
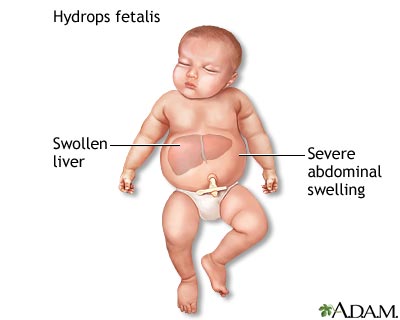
- Hydrops fetalis (Severe i.e. Hb <7 gm/dl ): 20-25%
- Severe anemia leads to tissue anoxia which causes:
- Placental hyperplasia: In effort to increase O2 supply
- Damage to liver: Due to extensive extramedullary hematopoiesis the liver is damaged is leading to hypoproteinemia, generalized edema, ascites and hydrothorax
- Fetal death: due to cardiac failure
- Prenatal transfusion may save the baby till maturity
- Severe anemia leads to tissue anoxia which causes:
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS
1. Maternal:
- History: Previous episodes of possible sensitization (Causes of feto-maternal bleed and prior Rh+ baby)
- ABO and Rh Blood groups of mother and father
- Antibody screening: Indirect Coomb’s test –
- If +ve: test serially for high titers of maternal anti-Rh IgG (Critical level: >1:16)
- If –ve at 12th week:
- Primigravida: Repeat at 28th and 36th week
- Multigravida: Repeat at monthly intervals from 24th week onwards
Indirect Coomb’s test: Incubation of known Rh(D) positive RBCs with maternal serum is the first step in the indirect Coombs test. Any anti-Rh(D) antibody present will adhere to the RBCs. The RBCs are then washed and suspended in serum containing antihuman globulin (Coomb’s serum). Red cells coated with maternal anti-Rh(D) will be agglutinated by the antihuman globulin, which is referred to as a positive indirect Coomb’s test.
Direct Coomb’s test is performed on the neonate’s RBCs after birth to detect the presence of maternal antibody on the RBCs. It is performed by placing the infant’s RBCs in Coomb’s serum; maternal antibody is present if the cells are agglutinated.
2. Fetal:
a. Serial Amniocentesis: for estimation of bilirubin in amniotic fluid
- Indications:
- Antibody titer >1:8
- Previous history of severely affected baby
- Heterozygous father
- Time:
- No history of previous affected baby: at 30-32 weeks and then repeat after 3-4 weeks
- History of previous affected baby: >/= 10 wks prior to the date of affection
- Analysis: Spectrophotometry of bilirubin contained amniotic fluid is done and plotting is done and optical density of the fluid at wavelength 450 nm is plotted in Liley’s chart (semilogarithmic scale vs gestational age). The deviation bulge obtained is directly proprtion to the severity.
3 Zones in Liley’s Chart
- Zone I: continue till term, baby unlikely to be affected
- Zone II: may require premature termination beyond 34 wks
- Zone III: severely affected baby. Imminent fetal death. Termination if >34 wks. If <34wks intrauterine transfusion repeatedly till 34 wks then terminate.
b. MCA Doppler peak velocity assessment: Alternative to Amniocentesis
c. Ultrasonography: Findings include –
- Polyhydraminos
- Fetal hepatosplenomegaly, Bowel wall edema (Extramedullary hematopoiesis)
- Cardiomegaly, pericardial effusion
- Scalp and limb edema
- Abnormal fetal posture (Buddha position)
- Sluggish fetal movement
- Placental hypertrophy and thickening
PREVENTION
300 mcg Rho-GAM (Anti-D Ig) i.m to mother (100 mcg neutralizes 5ml RBC) is given:
- At 28 weeks to Rh-ve mother if:
- Father is Rh+ve or father’s Rh status unknown
- Prior history of causes suggesting feto-maternal bleed
- Postpartum (within 72 hrs) if: Rh+ve fetus
- After abortion
If mother has been sensitized previously, administration of Rh IgG is of no value.
MANAGEMENT
- Unimmunized mothers: Expectant till term but not to exceed the expected date of delivery
- Immunized mothers:Severity assessment based on previous history of stillbirth, sudden rise in Antibody titer, Deviation bulge (Liley’s chart), Doppler and USG features of fetal affection-
- Mild: Wait till 38 weeks and terminate pregnancy
- Severe: Terminate pregnancy after determining lung maturity
- Care during delivery:
- Vaginal delivery: Careful fetal monitoring, Gentle handling of uterus in 3rd stage of labor and No prophylactic ergometrine
- Cesarean Section: Avoid blood spillage into peritoneal cavity and Manual removal of placenta
- Clamping umbilical cord: Quickly done and cord kept long (15-20cm) for exchange transfusion if needed
- Collection of cord blood for investigations: ABO and Rh blood group, Hb, Bilirubin, Direct Coomb’s test
- Intra-uterine transfusion:
- For severely affected fetus before 34 weeks
- O-ve blood compatible with mother and fetus given by intraperitoneal or intravascular approach
- Can be started at 18 wks, repeat at 1-3 wks interval upto 30-32 wks, then terminate pregnancy