Cranial Nerves : III,IV and VI
Occulomotor Nerve (Cranial Nerve III or CN III)
Functional Components:
- General Somatic Efferent (GSE)/ Somatic Efferent (SE)
- General Visceral Efferent (GVE)
Nuclei: situated at the midbrain
a. Main motor nuclei (GSE):
- At the level of superior colliculus
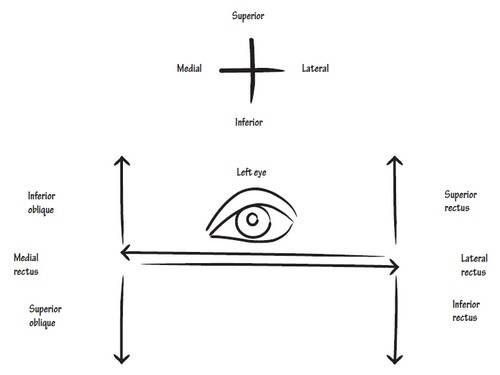
- Supplies all the extrinsic muscles of eye except the Superior oblique and the lateral rectus (Mnemonic: LR6SO4 rest 3)
b. Accesory Parasympathetic nucleus (GVE):
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus (E-W nucleus)
- Situated posterior to main motor nucleus
- Supplies intrinsic muscles of eye
E-W nucleus –> III nerve –> Nerve to inferior oblique –> Branch to ciliary ganglion –> Relay –> Short ciliary nerves supply ciliaris and constrictor pupillae muscles
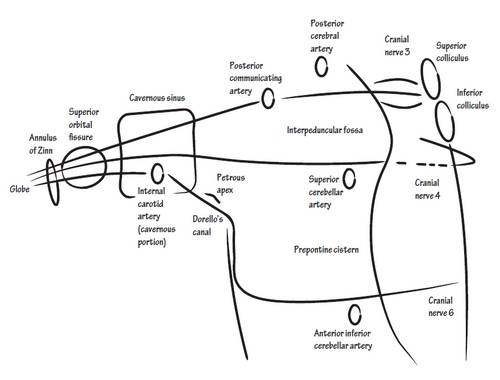
Course:

- Emerges on the anterior surface of the midbrain
- Enters the cavernous sinus and is placed in its lateral wall most anteriorly
- Divides into 2 divisions both of which pass through the middle part of superior orbital fissure
- Superior division supplies superior rectus and levator palpebrae superioris
- Inferior division supplies medial rectus, inferior rectus and inferior oblique
- Nerve to inferior oblique gives a branch for ciliary ganglion which supplies constrictor pupillae and ciliaris muscle
Lesion:
- Down and out eye: involvement of elevators of eye (inferior oblique and superior rectus)
- Ptosis : involvement of levator palpebrae (elevator of eyelid)
- Dilation of pupil and loss of accomodation : involvement of intrinsic muscles of eye
- Diplopia
- Lateral squint
Trochlear nerve (Cranial Nerve IV or CN IV)
Functional components:
- GSE/SE
Nucleus: situated at midbrain
- Lies inferior to the occulomotor nucleus at the level of inferior colliculus
- Supplies superior oblique muscle of eyeball
Course:
- Emerges from the posterior surface of the midbrain and immediately decussates
- Cavernous sinus
- Superior orbital fissure
- Innervates uperior oblique muscle
Lesion:
- Affected eye is hypertropic than the unaffected eye (involvement of superior oblique muscle)
- Diplopia (double vision) : To counteract the nauseating effect of diplopia, patients tilt their head to bring the eyes in the same plane
Abducent Nerve (Cranial Nerve VI or CN VI)
Functional components:
- GSE/SE
Nucleus: situated at pons
- Lies in the floor of 4th ventricle and beneath the facial colliculus
- Supplies lateral rectus muscle of eyeball
Course:
- Fibres pass anteriorly through pons
- Cavernous sinus
- Superior orbital fissure
- Innervates lateral rectus muscle
Lesion:
- Medial squint
- Diplopia with attempted far vision
Pictures from: Neuroanatomy – Draw it to know it by Adam Fisch