Delayed wound healing in Diabetes Mellitus
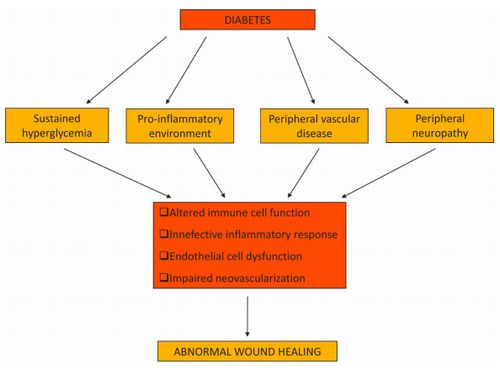
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a chronic disorder of glucose metabolism with hyperglycemia triggered by conditions associated with a relative or absolute insulin deficiency. Insulin is an anabolic hormone with profound effects on the metabolism of carbohydrate, fat and protein. Less severe hyperglycemia is called Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT) which is associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes in future. Here is a illustrative video to review your basics on process of wound healing.
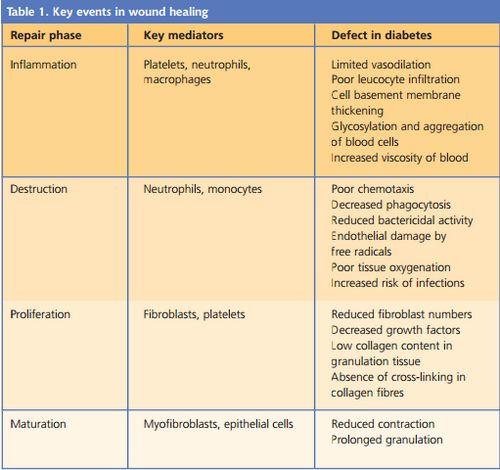
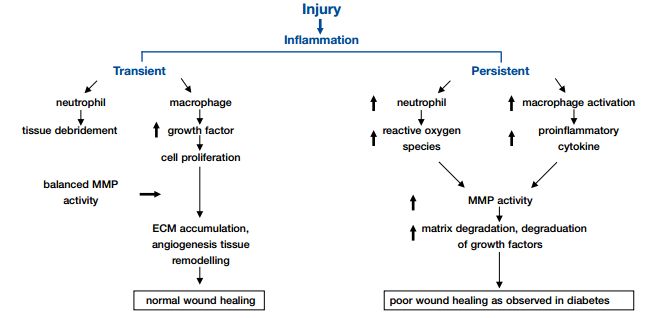
Delayed wound healing is a common complication of Diabetes Mellitus. In some cases, ulcers may require more than 6 months to heal and in extreme cases amputations may be required. Although there is no clear understanding of the mechanism involved, various researches have outlined the causes of delayed wound healing in diabetes mellitus as:
A. Delayed vascularization and reduction in blood flow:
- Atherosclerosis and other vascular changes in DM leads to impaired circulation leading to hypoxia and decreased nutrient supply at the wound site which in turn impairs wound healing.
- Hypoxia increases Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) which mediates the activation of caspase-3 leading to dysregulation of apoptosis and delayed wound healing.
B. Immunosupression:
- Dysfunction of neutrophil and monocyte chemotaxis
- In cases of oral wounds, decreased salivary flow rate and decreased scavengers like glutathione and melatonin play an important role
- Local infection
- Inhibited production of type I and type III collagen
- Increased collagenase called MMP-8 (Matrix Metalloproteinase 8)
C. Decreased Growth factors essential for wound healing:
- Decreased EGF (re-epithelialization), IGF (chemotaxis and fibroplasia), TGF-b and PDGF (chemotaxis, vasculariazation and ECM deposition) and NGF
D. Psychological stress
- Immune dysfunction
- Unhealthy habits including inadequate nutrition, alcohol abuse and cigarette smoking
- Hyperglycemia due to increased adrenaline and nor-adrenaline
E. Diabetic neuropathy
- Due to loss of sensation, wounds may not be noticed and neglected
Source:
- The Mechanism of Protracted Wound Healing on Oral mucosa (Yoshihiro Abiko and Denis Selimovic)