Common Diagnostic Procedures for Heart Diseases
Heart disease is responsible for 1 in every 4 deaths in the United States alone, making it the top cause of death for men and women. This condition, which primarily affects the heart, comes in different forms, including arrhythmia and coronary artery disease, which remains to be the most common type there is.
With alarming statistics, one may worry about their chances of having such condition. Typically, heart disease affects men and people of most ethnicities in the United States, such as Hispanics, Caucasians, and African Americans. However, it can affect anyone, and the only way to get ahead of this condition is through early diagnosis and prompt treatment. It’s important to educate yourself about heart disease in your treatment journey.
Diagnosing Heart Disease
If you have been experiencing symptoms of a heart problem, which include shortness of breath, chest pain and tightness, slow or fast heartbeat, fainting, or sudden swelling of the abdomen, legs, and feet, book an appointment with your doctor as soon as possible to have the problem diagnosed and treated as soon as possible.
During your consultation, your health-care provider will perform a series of evaluations and tests. These tests will also help screen you for heart disease before you start to develop any noticeable symptoms.
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram is one of the first tests that may be performed to determine the presence of heart disease. This quick, painless, and inexpensive test works by recording your heart’s electrical activity by attaching small electrode patches to the skin of your chest. Once the attachments are in place, the ECG will then record electrical impulses of the heart, assessing its rhythm and evaluating for certain abnormalities. It can also help to diagnose poor blood flow to the cardiac muscle and ultimately diagnose a heart attack.
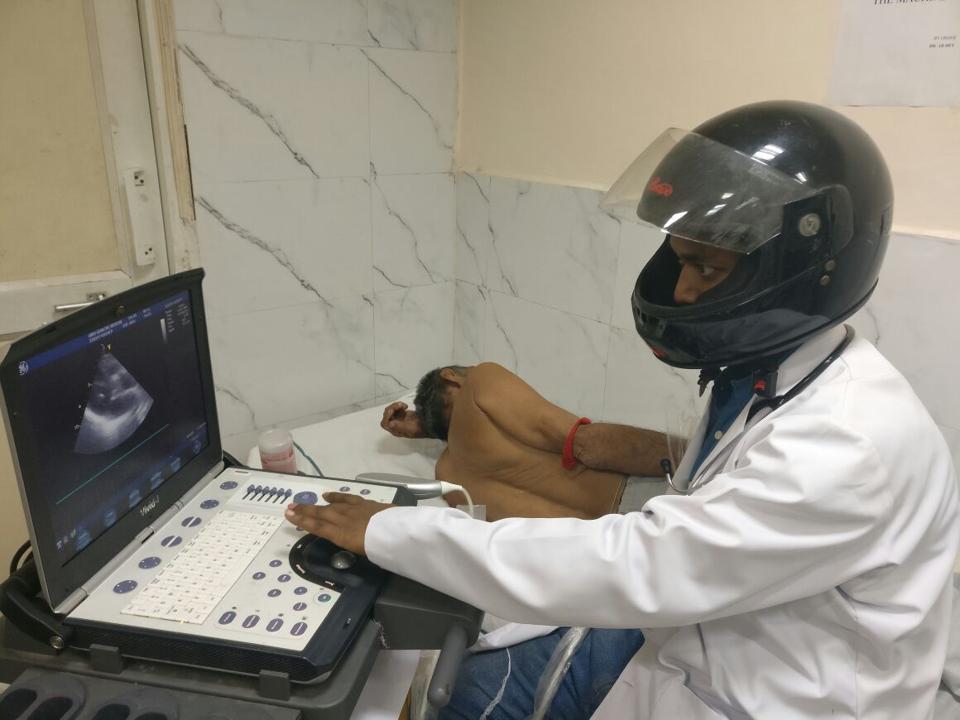
Echocardiogram
To diagnose a heart problem, you may be required to undergo an echocardiogram, which is basically an ultrasound of the heart. It allows a visualization of the heart’s chambers, walls, valves, and blood vessels that better identifies its condition, specifically, how the heart moves, how well it is pumping, its shape and size, the thickness and movement of its walls, and if there are any growths or regurgitation around its valves.
Cholesterol Test
Our bodies need cholesterol to function properly, but too much of it can lead to stroke, clogged arteries, and heart disease—which is why your doctor may request a complete cholesterol test or lipid profile to diagnose a heart problem. This blood test measures the levels of cholesterol and fat in your bloodstream, which also determines your risk of a heart attack. This diagnostic procedure is essential especially if you have a family history of heart disease, have diabetes, lead an inactive lifestyle, or are obese or overweight.
Stress Tests
Another common diagnostic procedure for heart disease is a stress test, which determines how well your heart functions during physical activity. These stress tests include an exercise stress test, which is basically performing an ECG during exercise. During this test, your doctor checks your blood pressure, heart rate, heart rhythm, and probably blood oxygen saturation through the use of a Nihon Kohden pulse oximetry sensor.
Another stress test is the stress echocardiogram, or what’s simply known as the stress echo. During this procedure, a tracer or a radioactive substance is injected into the bloodstream. Then, ultrasound is used to detect any abnormalities in the heart’s valves and chambers. A nuclear cardiac stress test, which is sometimes referred to as an exercise thallium scan, may also be done, which is another stress test that helps detect any damage to the heart muscle.
Reminders
While some types of heart problems are conveniently detected during a doctor’s appointment, some may be diagnosed in an emergency scenario, such as during a heart attack. Don’t wait until it’s too late. Have yourself checked regularly, especially if you are at risk. Meanwhile, it isn’t too late to make healthy changes in your lifestyle to prevent heart disease and its complications altogether.






