Meningitis : Causative Agents and Lab diagnosis
Presentation on Etiological factors and Laboratory Diagnosis of Meningitis
Objective 1:
- To list the important causative agents of meningitis.
TYPES OF MENINGITIS
- Acute Pyogenic Meningitis
- Aseptic Meningitis
- Chronic Meningitis
- Tuberculous
- Fungal
- Syphillitic
- Protozoal
- Helminthe
Causative agents of acute pyogenic meningitis
• Neonates
– Escherichia coli
– Group B streptococci
– Listeria monocytogenes
– Streptococcus pneumoniae
• Children
– Neisseria meningitidis
– Streptococcus pneumoniae,
– Haemophilus influenzae
• Adults
– Streptococcus pneumoniae,
– Neisseria meningitidis
• Elderly
– Listeria species
Causative Agents of Aseptic meningitis
• Common:
– Enteroviruses
– Herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV 2)
– Arthropod borne viruses (Tickborne, West Nile, Murray Valley, Japanese B)
– HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
• Less common
– Varicella zoster virus (VZV)
– Epstein Barr virus (EBV)
Causative Agents of Chronic Meningitis
Tuberculous meningitis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Syphillitic meningits
- Treponema pallidum
Fungal meningitis
• Cryptococcus neoformans (most common in HIV patients)
• Candida albicans
• Mucor species
• Aspergillus fumigatus
• Coccidioides immitis
• Histoplasma capsulatum
• Blastomyces dermatitidis
Protozoal
• Toxoplasma gondii
• Trypanosoma
• Acanthamoeba
Helminthes
• Taenia solium
Objective 2:
- To outline laboratory diagnosis of bacterial meningitis.
Specimens
- CSF
- Blood
- Sample
- Nasal swab
- Peticheal lesions
- Autopsy
A. Examination of CSF
Macroscopy
• CSF is cloudy under increased pressure and blood may be seen.
CSF is centrifuged and following methods are used:
- Microscopy
- Culture
Microscopy
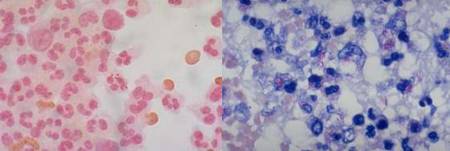
Unstained preparations: wet mounts
Stained smears:
- Common stains: Gram stain, Ziehl-Neelsen stain
- Fluorescent dyes: Acridine orange, Auramine rhodamine
Culture
Culture Media
- Enriched solid media- blood agar, chocolate agar
- Selective solid medium- MacConkey agar
- Robertson Cooked meat broth (for anaerobes)
Steps:
- CSF inoculated in culture media
- incubation at 35-36°C under 5-10% CO2
- Colonies appear after 18-24 hours, identified by morphology and biochemical reactions.
B. Blood culture
- incubated for 4-7 days, with daily subcultures
C. Nasopharyngeal Swab
• Useful for detection of carriers
• Done without contamination with saliva
D. Petechial lesions
Menigococci may be demonstrated by microscopy and culture
E. Autopsy
• Specimen from meninges, lateral ventricles, or surface of brain and spinal cord
• Within 12 hours of death of patient
• Smear or culture
Biochemical tests
• Catalase test
• Oxidase test
• Indole test
• Urease test
• Coagulase test
• Citrate Utilization test
• Triple sugar iron agar
Agglutination test:
- Direct slide agglutination test with specific antisera
- Latex agglutination test
- Immunoflourescence test
- Other rapid identification methods
- Molecular diagnosis – PCR test
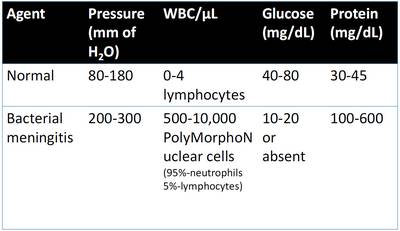
Various changes in Acute Pyogenic Meningitis:
References:
- Textbook of Microbiology
- Diagnostic Microbiology
Prepared and Presented for Correlation Seminar in Kist Medical College by:
|




1 Comment
i like it.
Comments are closed.